Investment Demand Curve: Definition, Factors & Examples
Investment Demand Curve: Definition, Factors & Examples
Blog Article
Definition of the Investment Demand Curve
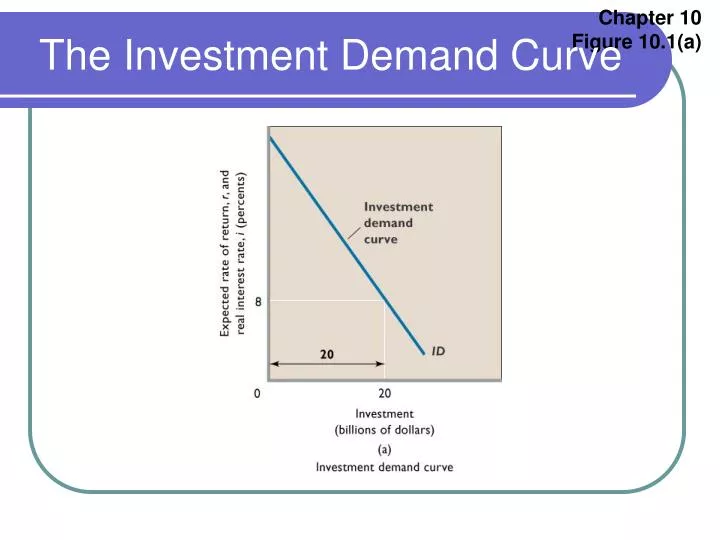
The investment demand curve is an economic concept that illustrates the relationship between the interest rate and the level of investment undertaken by businesses. It is a downward-sloping curve that reflects the inverse relationship between interest rates and investment levels. The basic principle behind the curve is that as interest rates decline, businesses are more inclined to invest in capital projects due to lower borrowing costs, whereas higher interest rates discourage investment.
The investment demand curve is a fundamental component of macroeconomic models, particularly in Keynesian economics, where investment plays a critical role in determining aggregate demand. It provides insights into how changes in interest rates, economic policies, and external factors influence business investment decisions.
Factors Affecting the Investment Demand Curve
Several factors influence the position and shape of the investment demand curve. These factors determine how responsive investment is to changes in interest rates and whether the curve shifts inward or outward.
1. Interest Rates
The most direct determinant of investment demand is the interest rate. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, encouraging firms to invest in projects with long-term payoffs. Conversely, higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, reducing the willingness of firms to invest.
2. Business Expectations and Confidence
If businesses expect strong economic growth and higher future profitability, they are more likely to invest, shifting the investment demand curve to the right. On the other hand, economic uncertainty, political instability, or market downturns may dampen business confidence, leading to a leftward shift in the curve.
3. Technological Advancements
Innovation and new technology can increase the expected returns on investment. Companies that adopt new production methods or invest in emerging industries may experience higher productivity, shifting the investment demand curve outward.
4. Corporate Tax Rates and Government Policies
Tax incentives, subsidies, and favorable regulatory policies can make investment more attractive. If the government lowers corporate tax rates or provides depreciation allowances, businesses may invest more, shifting the curve to the right. Conversely, higher taxes and stringent regulations may deter investment.
5. Availability of Credit and Financial Markets
A well-functioning financial system ensures businesses have access to capital. If banks and financial institutions are willing to lend at reasonable terms, investment increases. In contrast, during credit crunches or banking crises, firms may find it difficult to secure funding, reducing investment levels.
6. Cost and Productivity of Capital Goods
The price of machinery, equipment, and other capital goods affects investment decisions. If capital goods become cheaper due to improvements in production processes or trade policies, investment demand increases. Higher costs may discourage investment, shifting the curve to the left.
7. Inflation Expectations
Inflation can impact investment decisions. If businesses anticipate higher inflation in the future, they may invest more in the present to avoid rising costs later. However, if inflation leads to economic instability, firms may delay investment due to uncertainty.
8. Consumer Demand and Aggregate Demand
Strong consumer demand signals businesses that expanding production capacity is necessary, increasing investment. In periods of low consumer demand, firms may be reluctant to invest in new projects.
9. Global Economic Conditions
International trade conditions, global financial stability, and foreign direct investment trends influence investment demand. A strong global economy supports higher domestic investment, while global recessions or trade restrictions may have the opposite effect.
Examples of Investment Demand in Action
Example 1: Impact of Interest Rate Changes
Suppose the central bank lowers interest rates from 5% to 2%. A company considering an expansion project costing $10 million now finds it cheaper to finance the investment due to lower borrowing costs. As a result, the firm proceeds with the expansion, leading to an increase in aggregate investment. This scenario illustrates movement along the investment demand curve.
Example 2: Technological Advancements Driving Investment
A technology firm discovers a revolutionary production method that significantly reduces costs. Encouraged by the potential for higher returns, the firm invests heavily in new production facilities. This innovation leads to an outward shift in the investment demand curve.
Example 3: Government Policy Encouraging Investment
The government announces a new tax credit for companies that invest in renewable energy. As a result, multiple firms in the energy sector increase their investment in solar and wind power infrastructure. This policy-induced increase in investment shifts the investment demand curve to the right.
Example 4: Economic Uncertainty Reducing Investment
Amid fears of an impending recession, businesses delay expansion plans due to uncertainty about future profits. Even though interest rates remain low, firms hesitate to commit to long-term investments, shifting the investment demand curve to the left.
Conclusion
The investment demand curve is a crucial economic tool that helps analyze how businesses respond to changes in interest rates and other influencing factors. By understanding the determinants of investment demand, policymakers and economists can develop strategies to foster economic growth. Whether through interest rate adjustments, tax incentives, or technological advancements, investment demand remains a key driver of economic activity and business expansion. Report this page